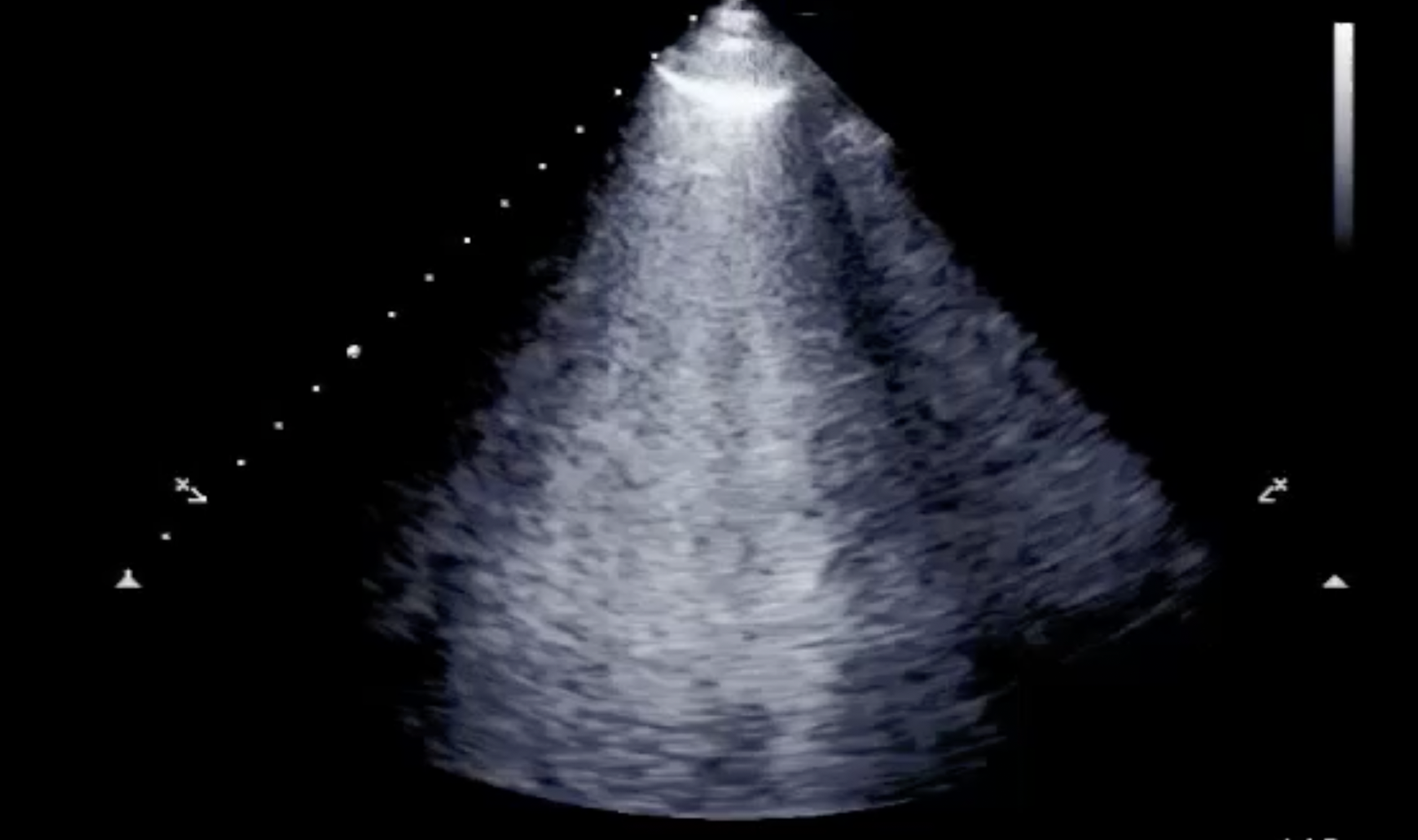
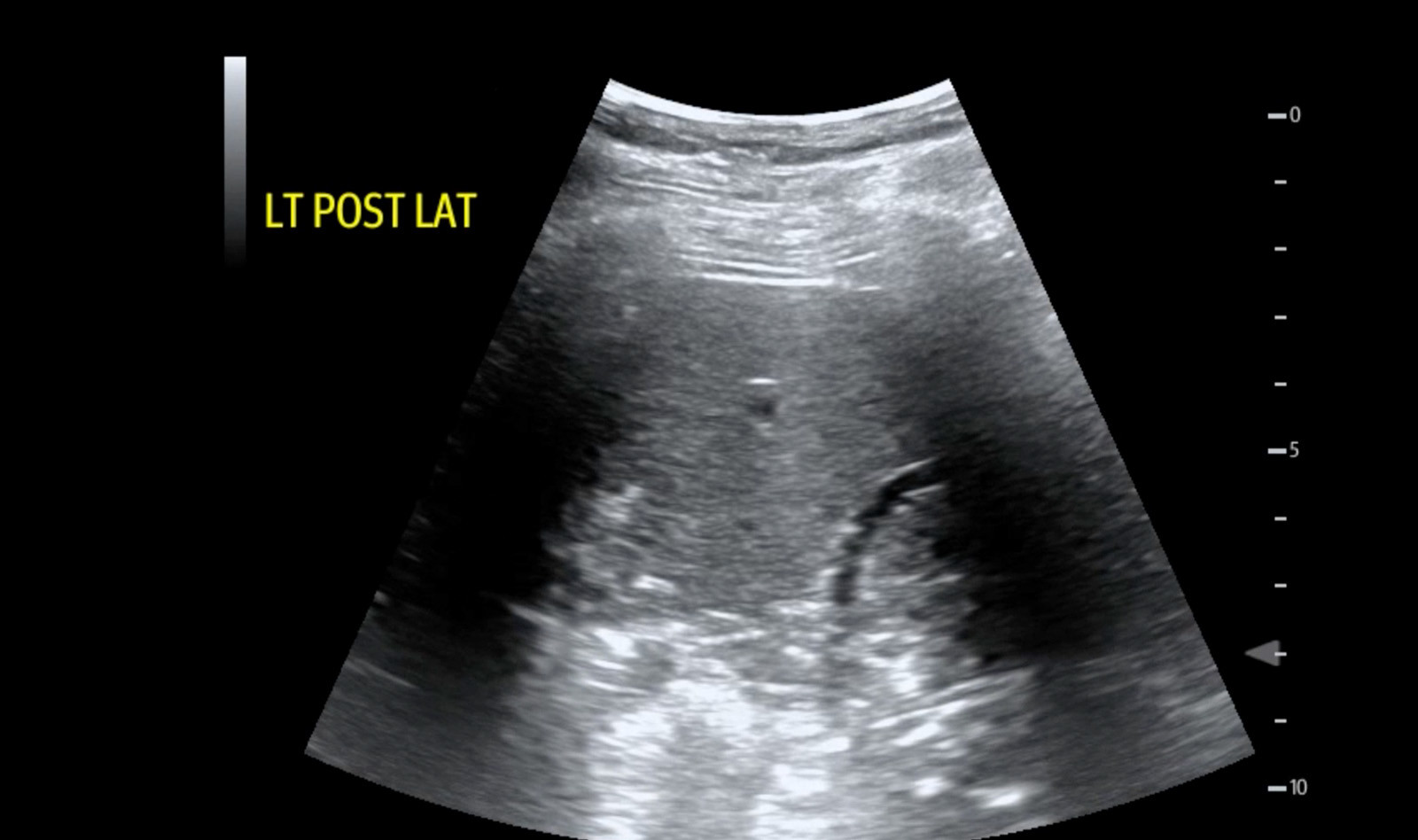
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN COVID-19 • The Predictive Role of Combined Cardiac and Lung Ultrasound in Coronavirus Disease 2019
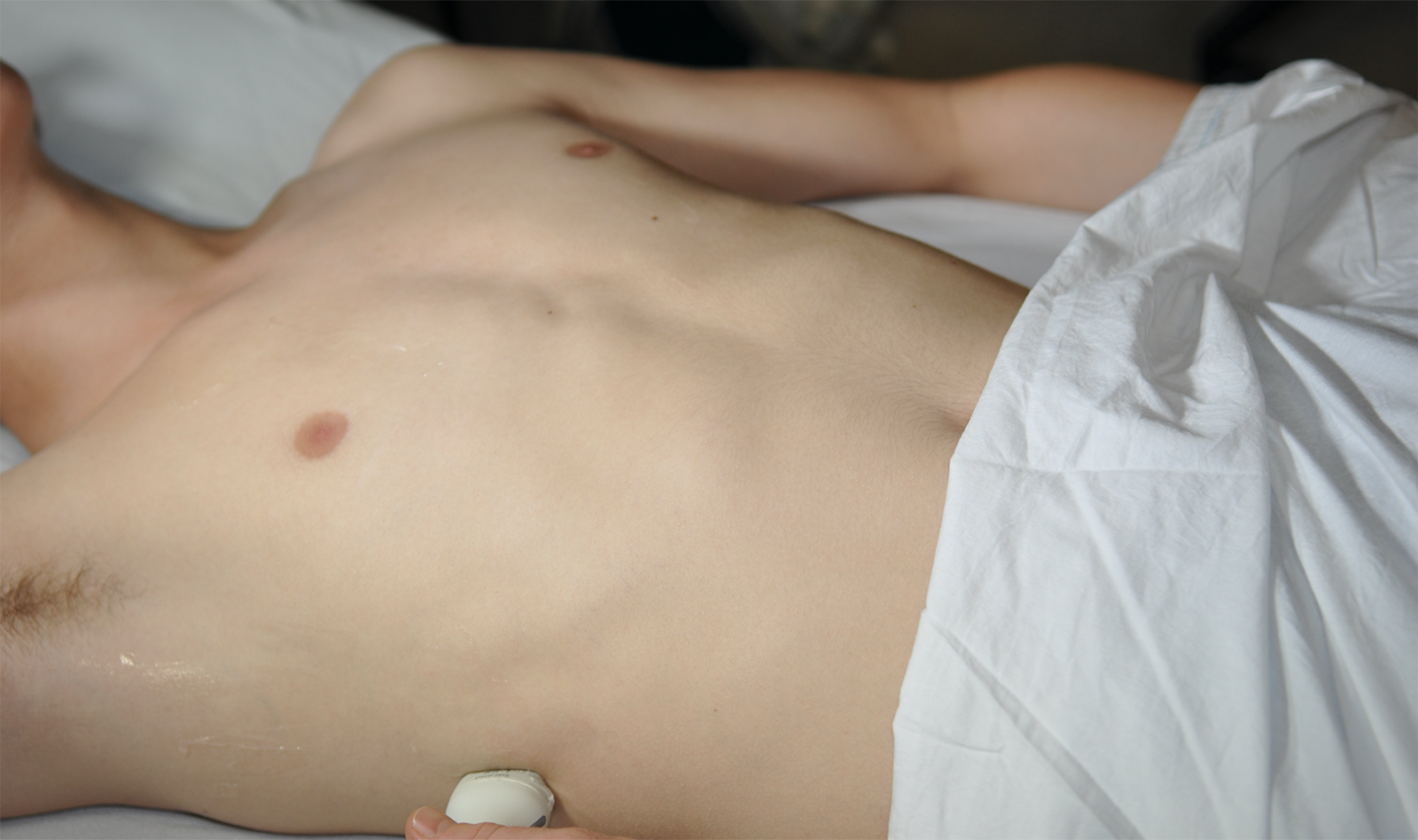
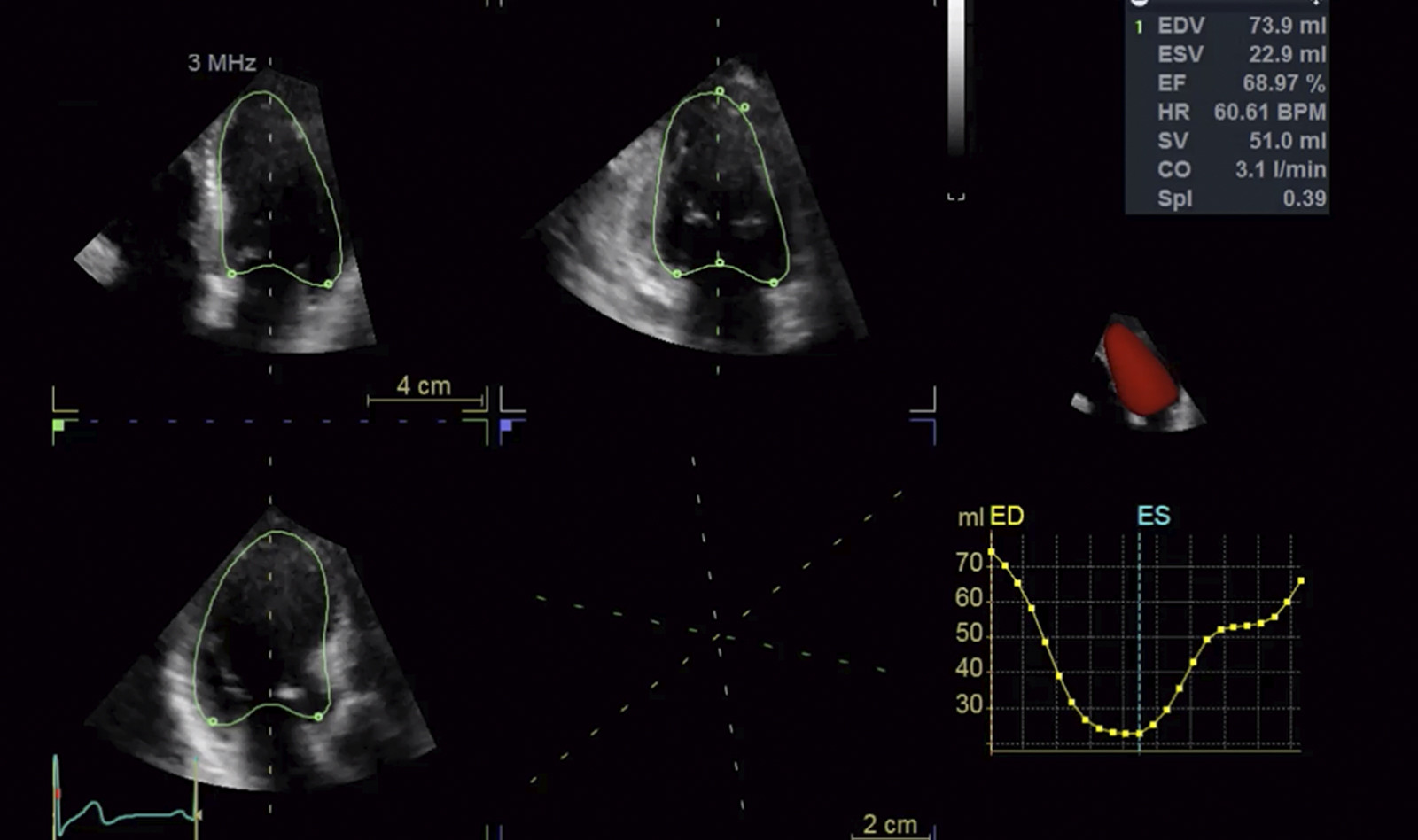
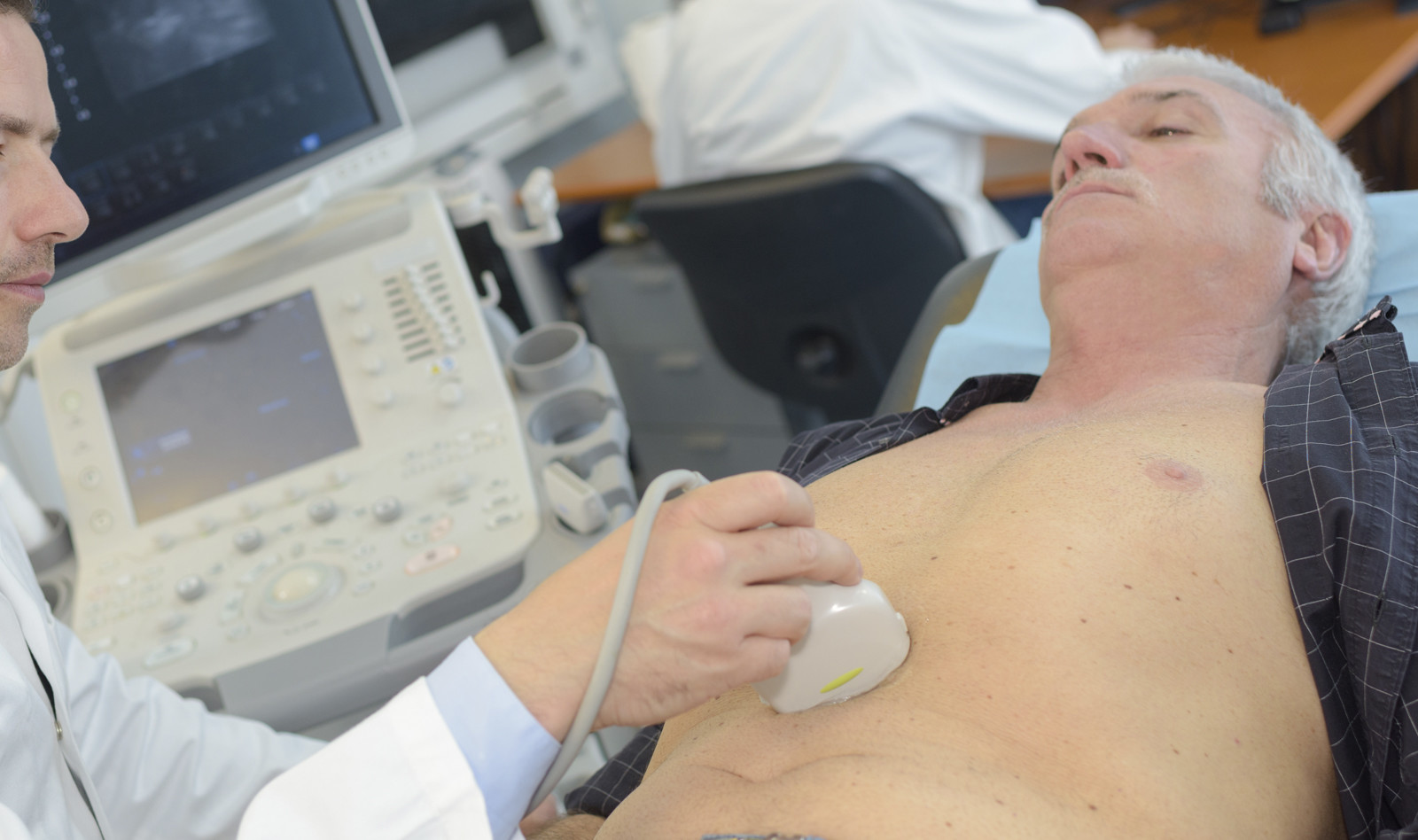
Despite the recognition of the prognostic significance and clinical implications of the cardiac complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), both the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging and the American Society of Echocardiography recommend limiting the echocardiographic assessme...
 English
English
 Español
Español